- Overview
- Installation
- Configuration
- Example models
- API reference
- Tips and tricks
- Hardware setup
Simple oscillator¶
This example implements a simple harmonic oscillator in a 2D neural population. Here, instead of having the recurrent input just integrate (i.e. feed the full input value back to the population), we have two dimensions which interact.
[1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import nengo
from nengo.processes import Piecewise
import nengo_loihi
nengo_loihi.set_defaults()
/home/travis/build/nengo/nengo-loihi/nengo_loihi/version.py:23: UserWarning: This version of `nengo_loihi` has not been tested with your `nengo` version (3.0.1.dev0). The latest fully supported version is 3.0.0
"supported version is %s" % (nengo.__version__, latest_nengo_version)
/home/travis/virtualenv/python3.6.3/lib/python3.6/site-packages/nengo_dl/version.py:42: UserWarning: This version of `nengo_dl` has not been tested with your `nengo` version (3.0.1.dev0). The latest fully supported version is 3.0.0.
% ((nengo.version.version,) + latest_nengo_version)
Creating the network in Nengo¶
Our model consists of one recurrently connected ensemble. The ensemble will naturally oscillate, but in order to begin the oscillation we make an input node to give it an initial kick.
[2]:
speed = 1.5 # Slower oscillations may decay to 0
with nengo.Network(label='Oscillator') as model:
ens = nengo.Ensemble(200, dimensions=2)
kick = nengo.Node(Piecewise({0: [1, 0], 0.1: [0, 0]}))
nengo.Connection(kick, ens)
nengo.Connection(ens, ens,
transform=[[1.0, speed], [-speed, 1.0]],
synapse=0.1)
kick_probe = nengo.Probe(kick)
ens_probe = nengo.Probe(ens, synapse=0.1)
Running the network in Nengo¶
We can use Nengo to see the desired model output.
[3]:
with nengo.Simulator(model) as sim:
sim.run(3)
t = sim.trange()
0%
0%
[4]:
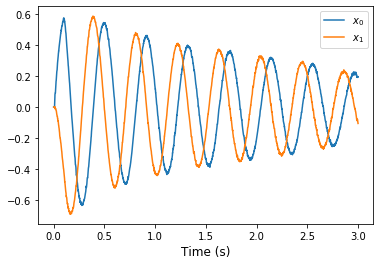
def plot_over_time(t, data):
plt.figure()
plt.plot(t, data[ens_probe])
plt.xlabel('Time (s)', fontsize='large')
plt.legend(['$x_0$', '$x_1$'])
plot_over_time(t, sim.data)
[5]:
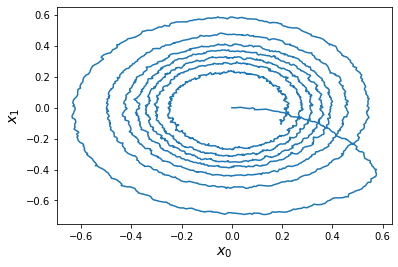
def plot_xy(data):
plt.figure()
plt.plot(data[ens_probe][:, 0], data[ens_probe][:, 1])
plt.xlabel('$x_0$', fontsize='x-large')
plt.ylabel('$x_1$', fontsize='x-large')
plot_xy(sim.data)
Running the network with Nengo Loihi¶
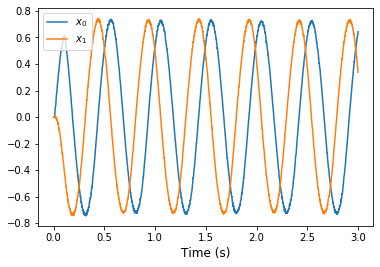
[6]:
with nengo_loihi.Simulator(model, precompute=True) as sim:
sim.run(3)
t = sim.trange()
/home/travis/build/nengo/nengo-loihi/nengo_loihi/discretize.py:471: UserWarning: Lost 1 extra bits in weight rounding
warnings.warn("Lost %d extra bits in weight rounding" % (-s2,))
[7]:
plot_over_time(t, sim.data)
[8]:
plot_xy(sim.data)
