Squaring the input¶
This demo shows you how to construct a network that squares the value encoded in a first population in the output of a second population.
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import nengo
Step 1: Create the Model¶
The model is comprised of an input ensemble (‘A’) and an output ensemble (‘B’), from which the squared value of the input signal can be decoded.
[2]:
# Create the model object
model = nengo.Network(label="Squaring")
with model:
# Create two ensembles of 100 leaky-integrate-and-fire neurons
A = nengo.Ensemble(100, dimensions=1)
B = nengo.Ensemble(100, dimensions=1)
Step 2: Provide Input to the Model¶
A single input signal (a sine wave) will be used to drive the neural activity in ensemble A.
[3]:
with model:
# Create an input node that represents a sine wave
sin = nengo.Node(np.sin)
# Connect the input node to ensemble A
nengo.Connection(sin, A)
# Define the squaring function
def square(x):
return x[0] * x[0]
# Connection ensemble A to ensemble B
nengo.Connection(A, B, function=square)
Step 3: Probe the Output¶
Let’s collect output data from each ensemble and output.
[4]:
with model:
sin_probe = nengo.Probe(sin)
A_probe = nengo.Probe(A, synapse=0.01)
B_probe = nengo.Probe(B, synapse=0.01)
Step 4: Run the Model¶
[5]:
# Create the simulator
with nengo.Simulator(model) as sim:
# Run the simulator for 5 seconds
sim.run(5)
[6]:
# Plot the input signal and decoded ensemble values
plt.figure()
plt.plot(sim.trange(), sim.data[A_probe], label="Decoded Ensemble A")
plt.plot(sim.trange(), sim.data[B_probe], label="Decoded Ensemble B")
plt.plot(
sim.trange(), sim.data[sin_probe], label="Input Sine Wave", color="k", linewidth=2.0
)
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.ylim(-1.2, 1.2)
[6]:
(-1.2, 1.2)
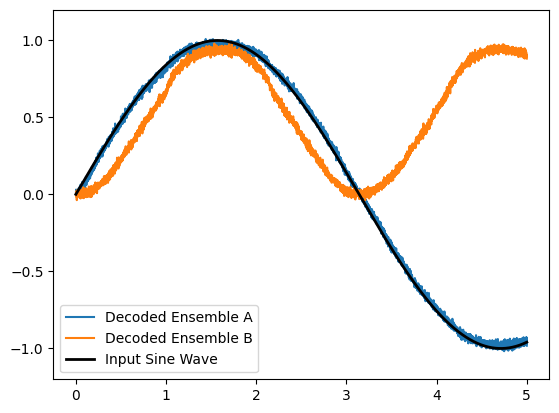
The plotted output of ensemble B should show the decoded squared value of the input sine wave.